Types of Psoriasis: How to Identify and Manage Each One
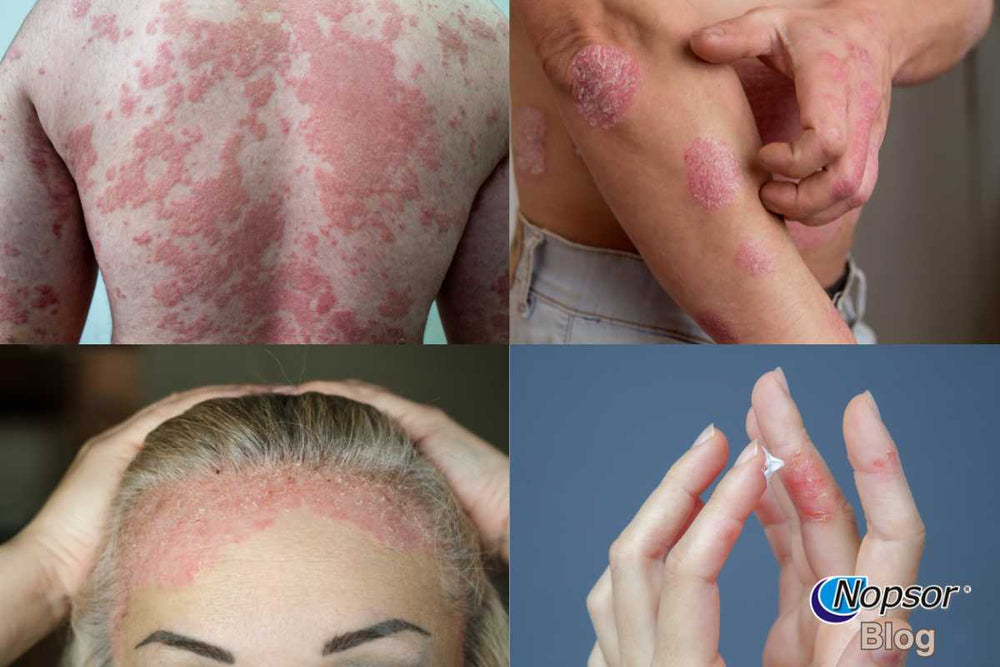
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While many recognize the classic symptoms—red, scaly patches on the skin—few realize that psoriasis comes in several distinct forms, each with its own characteristics and challenges. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper management and treatment.
1. Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris)
-
Prevalence: The most common type, affecting about 80-90% of people with psoriasis.
-
Symptoms: Raised, inflamed, and scaly patches (plaques) that commonly appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
-
Treatment Options: Topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, and biologic treatments.
2. Guttate Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: The second most common form, often triggered by infections like strep throat.
-
Symptoms: Small, red, drop-like spots that usually appear on the trunk, arms, and legs.
-
Treatment Options: Antibiotics (if triggered by infection), light therapy, and topical treatments.
3. Inverse Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: Less common but significantly impacts those who have it.
-
Symptoms: Smooth, red, shiny patches in skin folds (under breasts, around genitals, armpits).
-
Treatment Options: Topical steroids, antifungal treatments (if fungal infections coexist), and biologics.
4. Pustular Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: Rare but serious, often requiring medical attention.
-
Symptoms: White pustules surrounded by red, inflamed skin; can appear in localized areas (palms/soles) or cover the whole body.
-
Treatment Options: Systemic medications (such as retinoids or biologics), and hospitalization in severe cases.
5. Palmoplantar Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: Affects the hands and feet specifically.
-
Symptoms: Thickened, cracked skin on the palms and soles; may involve painful fissures.
-
Treatment Options: Salicylic acid, coal tar, and biologics.
6. Nail Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: Occurs in about 50% of people with psoriasis.
-
Symptoms: Pitting, thickening, yellowing, and detachment of the nails.
-
Treatment Options: Topical steroids, nail care routines, and systemic treatments for severe cases.
7. Scalp Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: Affects nearly half of people with psoriasis.
-
Symptoms: Flaky, silvery-white scales on the scalp, sometimes extending to the forehead or neck.
-
Treatment Options: Medicated shampoos (coal tar or salicylic acid), corticosteroids, and phototherapy.
8. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
-
Prevalence: The rarest but most severe form.
-
Symptoms: Widespread, severe redness, shedding of skin layers, fever, and systemic illness.
-
Treatment Options: Immediate hospitalization, systemic medications, and supportive care.
9. Psoriatic Arthritis
-
Prevalence: About 30% of people with psoriasis develop joint inflammation.
-
Symptoms: Joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and nail changes.
-
Treatment Options: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics.
Managing Psoriasis Effectively
While there is no cure for psoriasis, managing triggers and following a consistent treatment plan can help control flare-ups. Here are some key strategies:
-
Identify Triggers: Stress, infections, cold weather, and certain foods can exacerbate symptoms.
-
Use the Right Treatments: Consult a dermatologist to determine the best regimen for your type.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Healthy diet, regular exercise, and moisturizing can support skin health.
-
Explore Alternative Therapies: Some people find relief in natural treatments like coal tar, aloe vera, and dietary changes.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types of psoriasis is essential for effective treatment and symptom management. If you experience new or worsening symptoms, consult a healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
References:
-
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS):
- This resource offers comprehensive insights into different psoriasis types, including plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/psoriasis
-
National Psoriasis Foundation:
- This foundation provides detailed descriptions of psoriasis types, common locations, and visual aids to help identify each type.
- https://www.psoriasis.org/locations-and-types
-
Mayo Clinic:
- The Mayo Clinic offers an in-depth look at psoriasis, covering symptoms, causes, and detailed descriptions of various types.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/psoriasis/in-depth/psoriasis-pictures/art-20546858
-
Healthline:
- Healthline provides a visual guide to eight different types of psoriasis, detailing symptoms and treatment options.
- https://www.healthline.com/health/photos-types-psoriasis


Leave a comment
Also in Types of Psoriasis
Inverse Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Best Treatments
March 03, 2025
Inverse psoriasis causes smooth, red lesions in skin folds, leading to discomfort. Learn about its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments, including Nopsor Topical Treatment
Continue reading
Palmoplantar Pustulosis vs. Palmoplantar Psoriasis
February 13, 2025
Palmoplantar Pustulosis (PPP) and Palmoplantar Psoriasis (PP) are often confused due to their similar appearance on the hands and feet. However, they have distinct symptoms, triggers, and treatment approaches. While PPP is characterized by pus-filled blisters and strong links to smoking, PP manifests as thick, scaly plaques caused by an overactive immune system. This in-depth guide explores their differences, best treatment options, and lifestyle tips to help manage symptoms effectively. Whether you're struggling with flare-ups or seeking a proper diagnosis, this article provides expert-backed insights for clearer, healthier skin.
Continue reading
Palmoplantar Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
February 13, 2025
Palmoplantar psoriasis is a challenging condition that affects the hands and feet, causing thick, scaly skin, painful cracks, and discomfort in daily life. Understanding the symptoms, triggers, and treatment options is essential for effective management. This comprehensive guide explores the best medical and natural treatments, daily care routines, and practical strategies to reduce flare-ups. Whether you’re looking for relief through skincare, lifestyle changes, or medical therapies, this article provides expert-backed insights to help you regain comfort and confidence
Continue reading